Authors:
(1) Gopal Yadav, Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology & Chennai Mathematical Institute.
Table of Links
Brief Review of Wedge Holography
Emerging Multiverse from Wedge Holography
Application to Information Paradox
Application to Grandfather Paradox
Acknowledgements and References
2 Brief Review of Wedge Holography
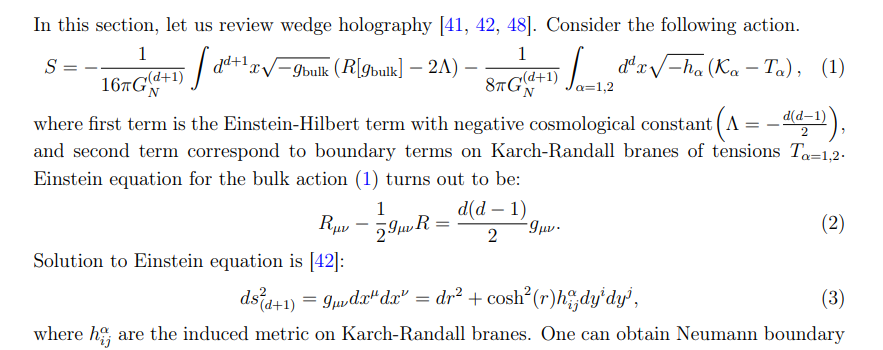
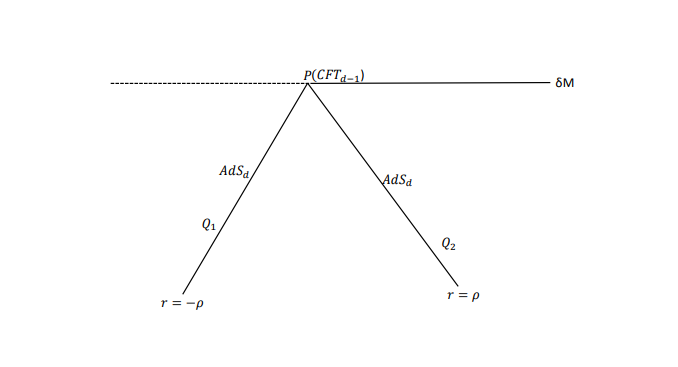
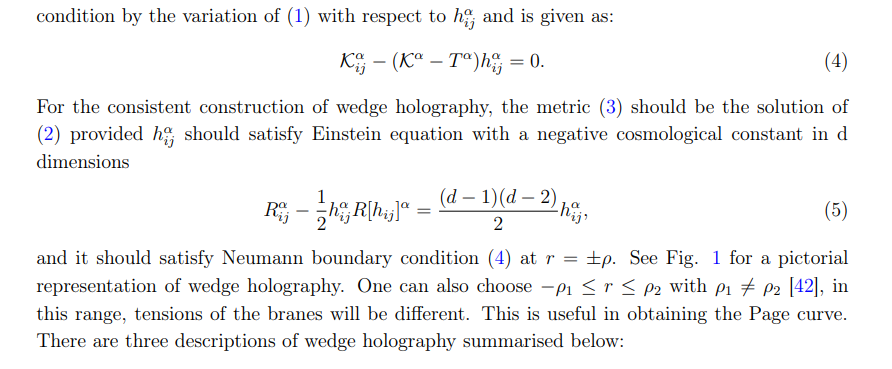
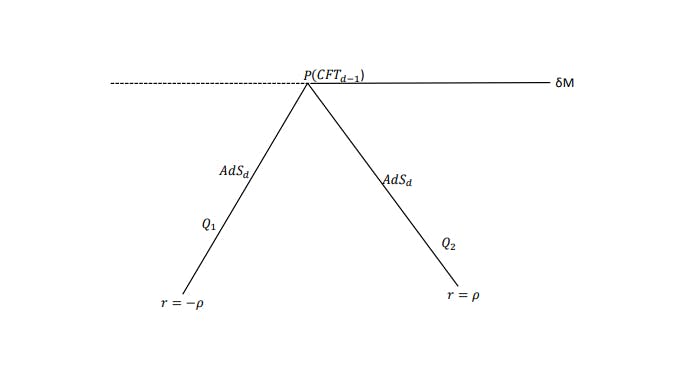
• Boundary description: CF Td−1 living on the wedge of common boundaries of two AdSd’s.
• Intermediate description: Two Karch-Randall branes of geometry AdSd (Q1 and Q2) glued to each other at the interface point by a transparent boundary condition.
• Bulk description: Einstein gravity in (d + 1)-dimensional bulk, AdSd+1.
Precisely, correspondence can be interpreted as: “Classical gravity in (d + 1)-dimensions has a holographic dual theory on the defect which is CFT in (d − 1)-dimensions”.
Wedge holography is useful in the computation of the Page curve of black holes. Let us understand this connection. In the intermediate description, we consider a black hole on Q2 whose Hawking radiation will be collected by weakly gravitating bath Q1 (i.e., T1 < T2). To calculate the entanglement entropy in the intermediate description, one is required to use the semiclassical formula:

where γ is the minimal surface in bulk. In wedge holography, there is one more extremal surface, Hartman-Maldacena surface [30], which starts at the defect, crosses the horizons, and meets its thermofield double. By plotting the entanglement entropies contributions of these surfaces, we can get the Page curve [2].
This paper is available on arxiv under CC 4.0 license.